As of 2017, the vision of the Internet of things (IoT) has evolved due to a convergence of multiple technologies, including wireless communication, real-time analytics, machine learning, commodity sensors, and embedded systems. Traditional systems like wireless sensor networks, control systems, automation (including home and building automation), and others all contribute to enabling the Internet of things.
The term 5G refers to a fifth-generation wireless and data network. Currently, we rely on a 4G network, which for the most part, is sufficient for basic data streaming and wireless communications. But for the Internet of Things to reach its full potential, a more capable, more universal and more accessible network is required. In other words, we need 5G technology before we can reach the next level of a fully connected world.
For 5G technology to become a reality, updates in infrastructure, mobile technology, sensor technology, processor technology and other areas must first be made. Companies like Qualcomm are spearheading this effort, and the first official 5G launches will come in 2018, with broad deployment in 2019.
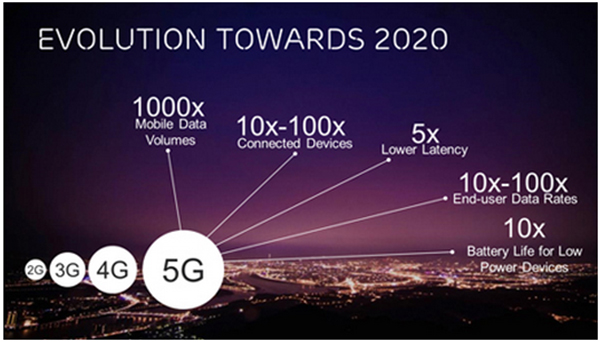
What to Expect with 5G Wireless
- Up to 10 Gbps connections to end points in the field
- 1 millisecond end-to-end round-trip delay
- 1,000x bandwidth per unit area
- Up to 100x number of connected devices
- Up to 99.999 percent availability
- Up to 100 percent coverage
- 90 percent reduction in network energy usage
- Up to 10-year battery life for low-power, machine-type devices
There is little doubt that 5G technology will connect many more devices. Right now, 4G modules are expensive, power-consuming, and demand complicated service plans, so much of the Internet of Things has stuck with either Wi-Fi and other home technologies for consumers, or 2G for businesses. 5G networks will accept small, inexpensive, low-power devices, so they’ll connect a lot of smaller objects and different kinds of ambient sensors to the internet.
Transportation and virtual augmented reality will benefit the most from 5G technology. As phones transform into devices meant to be used with VR headsets, the very low latency and consistent speeds of 5G will give users an internet-augmented world. The small cell aspects of 5G may also help with in-building coverage, as 5G encourages every home router to become a cell site.
Future Possibilities
Imagine a world in which self-driving cars, leveraging electric power for their journey, travel with millimeter precision to their destination — the effect would be fewer road blocks, traffic delays and accidents, plus more-efficient driving manners. This type of efficiency is only possible with a network capable of supporting millions of connected devices (in this case, the cars) at once. Such efficiency (particularly when paired with zero-emission technology) could improve air quality while drastically reducing consumption of fossil fuels. And that’s just one example of how 5G technology may power the future.




